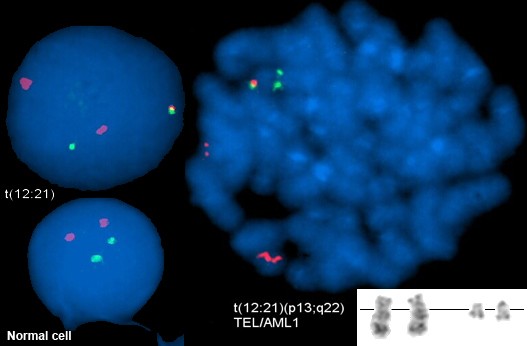
The t(12;21) translocation leads to the formation of the TEL(ETV6)/AML1(RUNX1) hybrid gene and provides an indication of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). It is the most common chromosomal aberration in childhood B-ALL (21% of cases) and has generally a good prognosis. This is a cryptic translocation and a difficult one to reveal by means of classic cytogenetic analysis.
This test is useful for patients with hemopoietic disorders for the diagnosis and/or confirmation of chronic and acute leukemia, for evaluation of remission or relapse or even after bone marrow transplantation for evaluation of recurrence of the disorder. The translocation is detected through FISH, using specific custom-labeled DNA probes, from at least 100 bone marrow cell nuclei.
This test may also be applied in combination with:
- Karyotype analysis of bone marrow cells, combined with molecular detection of multiple chromosomal rearrangements
- Multicolor karyotype (M-FISH)